Sky temperature
Radiation is a heat transfer mechanism, along with conduction, convection and phase change. All bodies which are hotter than 0°K emit thermal radiation. They also absorb thermal radiation emitted by their surroundings. The difference in the total amount of radiation emitted and absorbed by a body at any given moment may result in a net heat transfer which will produce a change in the temperature of that body.
Thermal radiation includes all those wavelengths of the electromagnetic spectrum which will heat a body when absorbed by it, ranging from about 100nm to 100,000nm. In general, the higher the temperature of a body, the lower the average wavelength of the radiation it emits. The range of terrestrial temperatures experienced within the built environment is relatively small, and relative to the temperature of the sun this range is ‘cold’ and so radiating at a ‘long’ wavelength compared to the sun. This anomaly allows us to categorise thermal radiation as short-wave solar radiation and terrestrial or long wave infra-red radiation.
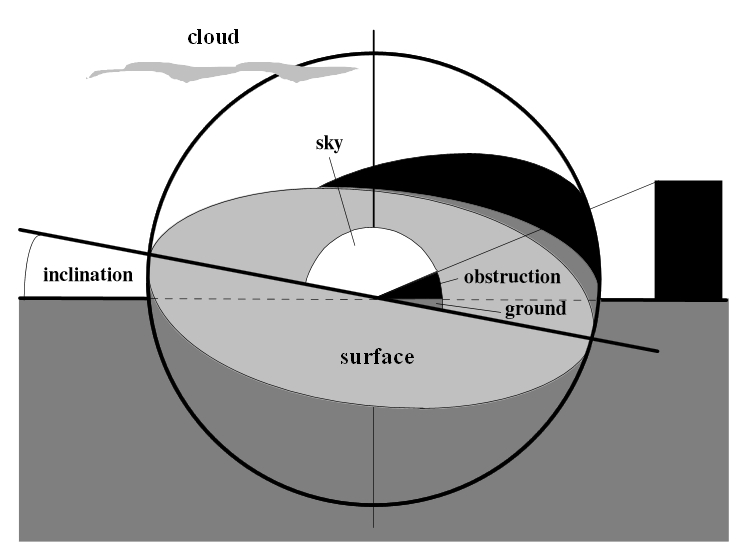
Terrestrial surfaces exchange long wave infra-red radiation in all directions within a hemisphere about their azimuth. This hemisphere can include a wide variety of thermal bodies, ranging from the sky to the ground and solid bodies, such as buildings, all of which will be emitting different intensities and wavelengths of thermal radiation themselves. In order to simplify this complex situation terrestrial radiation is generally treated as an average heat transfer based on hemispherical emissivities and average hemispherical surface temperatures.
The exchange of long wave infra-red radiation between a surface and the sky will depend on the exposure of the body to it, which may be affected by the angle of inclination, the extent to which it is obstructed, for example by other buildings, and the sky temperature.
The temperature in outer space approaches absolute zero at around 3 Kelvin, or -270°C. However, the atmosphere of the earth contains gases such as carbon dioxide, water vapour and other particles, which themselves emit long wave infra-red radiation, increasing the effective sky temperature.
This means that at any given location, the sky temperature will depend on variables such as altitude, humidity, cloud cover and the presence of other particles in the air such dust or pollution.
Under cloudless conditions in the desert, sky temperatures close to -50°C are commonly recorded, whilst in humid, cloudy conditions in countries such as Thailand, sky temperatures might be close to 20°C. Very broadly, the average sky temperature is likely to be near to 0°C.
An infrared thermometer can be used to measure the sky temperature. But care must be taken over the direction it is pointed, and how an average is determined. A different reading will be given depending on whether the temperature is measured at the zenith, where there is less atmosphere between the thermometer and space, or close to the horizon, and whether the temperature of a cloud is recorded or of the clear sky.
The sky temperature can be calculated for a given location if the amount of cloud cover is known. This can be estimated, or during the day, can be calculated by comparing the intensity of monitored horizontal global solar radiation with that amount which would theoretically have been recorded if the sky were perfectly clear.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
- Albedo.
- Cool roof.
- Dry-bulb temperature.
- Electromagnetic spectrum.
- Emissivity.
- Globe temperature.
- Mean radiant temperature.
- Operative temperature.
- Predicted mean vote.
- Psychometric chart.
- Running mean temperature.
- Sling psychrometer.
- Solar reflectance index.
- Temperature
- The thermal behaviour of spaces enclosed by fabric membranes.
- Thermal comfort.
- Thermal indices.
- Thermal optical properties.
- Thermal pleasure in the built environment.
- Urban heat islands.
- Wet-bulb globe temperature.
- Wet-bulb temperature.
Featured articles and news
Managing building safety risks
Across an existing residential portfolio, a client's perspective.
ECA support for Gate Safe’s Safe School Gates Campaign.
Core construction skills explained
Preparing for a career in construction.
Retrofitting for resilience with the Leicester Resilience Hub
Community-serving facilities, enhanced as support and essential services for climate-related disruptions.
Some of the articles relating to water, here to browse. Any missing?
Recognisable Gothic characters, designed to dramatically spout water away from buildings.
A case study and a warning to would-be developers
Creating four dwellings... after half a century of doing this job, why, oh why, is it so difficult?
Reform of the fire engineering profession
Fire Engineers Advisory Panel: Authoritative Statement, reactions and next steps.
Restoration and renewal of the Palace of Westminster
A complex project of cultural significance from full decant to EMI, opportunities and a potential a way forward.
Apprenticeships and the responsibility we share
Perspectives from the CIOB President as National Apprentice Week comes to a close.
The first line of defence against rain, wind and snow.
Building Safety recap January, 2026
What we missed at the end of last year, and at the start of this...
National Apprenticeship Week 2026, 9-15 Feb
Shining a light on the positive impacts for businesses, their apprentices and the wider economy alike.
Applications and benefits of acoustic flooring
From commercial to retail.
From solid to sprung and ribbed to raised.
Strengthening industry collaboration in Hong Kong
Hong Kong Institute of Construction and The Chartered Institute of Building sign Memorandum of Understanding.
A detailed description from the experts at Cornish Lime.